AI image generation is revolutionizing the way we create visual content, transforming simple text prompts into stunning images within seconds. This technology has democratized creativity, enabling anyone with an internet connection to produce professional-quality images without the need for traditional design skills.
Generative AI Examples Across Industries show just how versatile and powerful this technology has become. From fashion to advertising, businesses are leveraging AI to produce visuals that would have once required a team of skilled designers.
However, as AI-powered image generation becomes more sophisticated and accessible, it raises important ethical questions. From copyright concerns to the impact on creative professionals, understanding the ethical landscape of AI image generation is crucial for anyone using or considering this technology.
Listen To The Podcast Now!
Understanding the Technology Behind AI Image Generation:
Before diving into the ethical considerations, it’s important to grasp how AI image generation works.
These systems are powered by advanced machine learning models trained on vast datasets containing millions of images scraped from the internet.
The AI learns patterns, styles, and relationships between visual elements and text descriptions. When a prompt is entered, the system generates new images based on these learned patterns.
While this process is impressive, it lies at the heart of many ethical debates. The datasets often include copyrighted artwork, photographs, and designs created by human artists without their consent.
This raises crucial questions about ownership, consent, and fair compensation for artists in the digital age.
Copyright and Intellectual Property Concerns:
One of the most contentious issues surrounding AI image generation is copyright infringement. AI tools trained on copyrighted material without permission create a legal gray area.
Artists argue that their work is being exploited without compensation or credit, while AI companies claim that their use falls under fair use or transformative work.
Several lawsuits have been filed by artists and photographers, who accuse AI companies of unauthorized use of their work in training datasets.
Since copyright laws weren’t designed to address the complexities of AI, there’s significant legal uncertainty, which poses risks for both creators and users of AI-generated content.
For businesses and content creators using AI image generation, this uncertainty is a major concern.
If you use AI-generated images commercially, there’s a risk of facing legal action if the generated images are too similar to copyrighted work.
It’s important to understand the terms of service of the AI tool you use and consider the potential legal implications.
The Impact on Artists and Creative Professionals:
As AI image generation becomes more widespread, many artists, illustrators, and designers worry about the impact on their livelihoods.
Some fear that clients will prefer cheap or free AI-generated images over hiring human creators. This concern is valid, as we’re already seeing companies reduce their creative budgets in favor of AI tools. However, the reality is more complex.
While AI can generate generic images quickly, it still struggles with complex, specific creative requirements that demand human creativity, cultural awareness, and emotional intelligence.
The most successful approach seems to be collaboration, where AI tools augment human creativity rather than replace it entirely.
Artists are also finding ways to adapt by offering services that AI cannot provide, such as personalized consultations, brand strategy, and a unique perspective based on human experience.
Many artists are incorporating AI into their workflows, using it to speed up certain processes while maintaining creative control over the final product.
AI graphic design tools, for instance, are helping designers explore new creative avenues while preserving the artistic integrity of their work.
AI Training Data Bias and Representation:
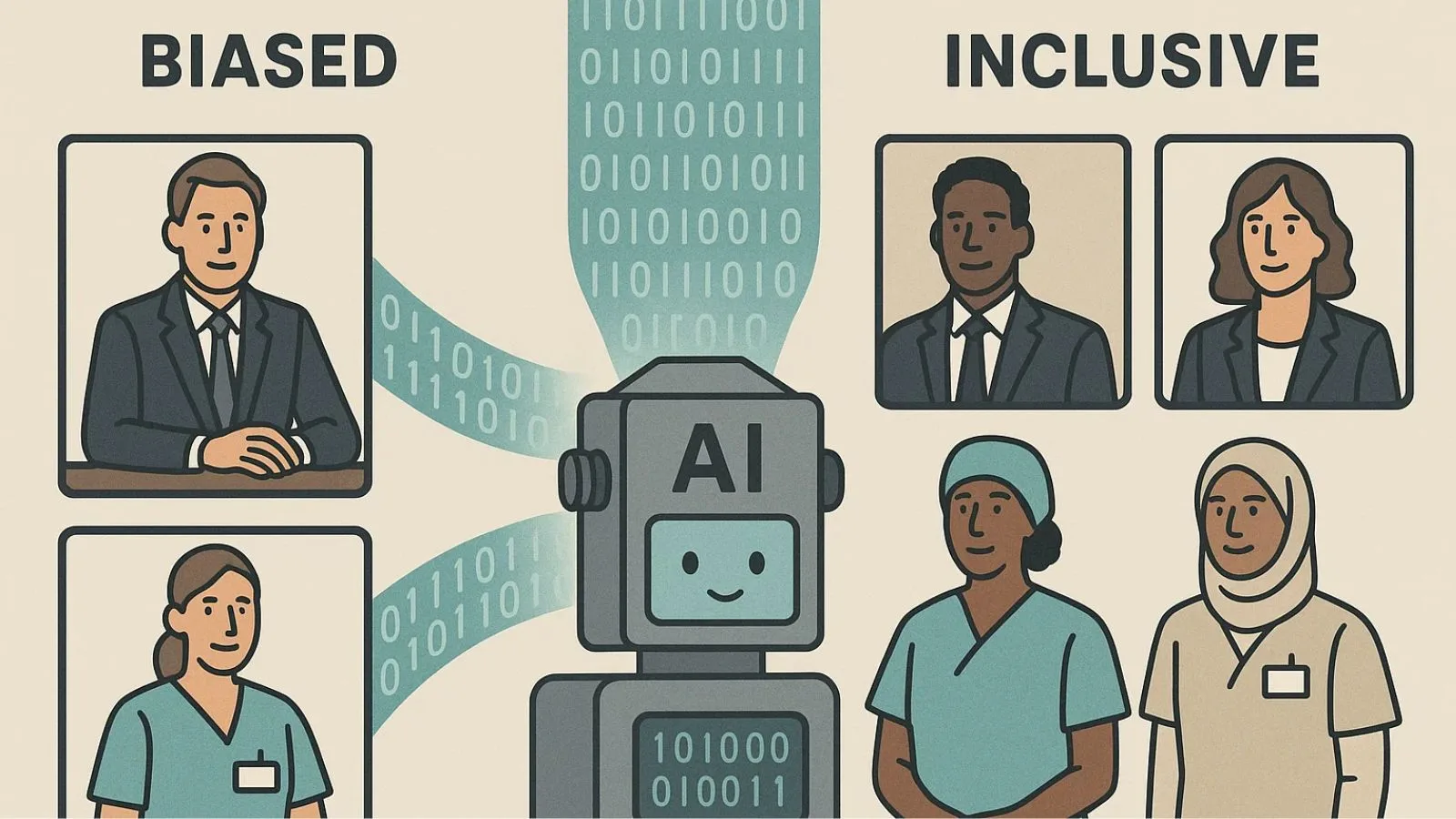
AI image generation systems reflect the biases present in their training data.
If the dataset predominantly features certain demographics, artistic styles, or cultural perspectives, the AI will reproduce and potentially amplify these biases. This can lead to problematic stereotypes and limited representation.
For instance, early AI systems often produced images that reinforced gender stereotypes or failed to represent diverse ethnicities.
When asked to generate images of a “CEO” or “nurse,” these systems often defaulted to stereotypical, biased representations. This is a critical issue for businesses committed to diversity and inclusion.
Using AI-generated images without critical evaluation could perpetuate harmful stereotypes in marketing, educational materials, or other public-facing communications.
Misinformation and Deepfakes:
The ability of AI image generators to create photorealistic images raises serious concerns about the spread of misinformation.
Fake images of non-existent events, doctored photos of public figures, and fabricated “evidence” can be created with minimal effort.
This capability adds another layer of complexity to an already misinformation-prone digital landscape.
The risks extend beyond politics and news. AI-generated images can be used for fraud, harassment, and reputation damage.
Creating fake compromising photos, fabricating reviews with AI-generated images, or manufacturing false evidence are frighteningly accessible possibilities. To combat this, platforms and tools need robust safeguards to prevent misuse.
Watermarking AI-generated content and developing detection tools are partial solutions, but they’re constantly in a race with AI’s improving generation capabilities.
Privacy and Consent Concerns:
When AI tools use images of real people, whether celebrities or ordinary individuals—there are significant privacy concerns.
People’s likenesses can be used to generate new images without their knowledge or consent. This becomes particularly troubling when AI systems generate images of individuals in situations they never participated in.
Additionally, AI tools may reproduce specific images from their training sets, especially if those images appear multiple times in the dataset.
This means private or sensitive images could potentially be reconstructed if someone uses the right prompts.
Currently, there’s little recourse for individuals who are concerned about their images being included in AI training datasets, as opt-out mechanisms are rare.
This power imbalance between technology companies and individuals needs to be addressed through regulation and ethical AI development.
Environmental Impact:
An often-overlooked ethical dimension of AI image generation is its environmental cost.
Training large AI models requires massive computational resources, consuming huge amounts of electricity and contributing to carbon emissions.
While generating a single AI image requires relatively little energy, the cumulative effect of billions of AI-generated images worldwide is significant.
As climate change continues to be a global issue, the environmental impact of AI technologies deserves attention.
Companies developing AI tools should be transparent about their energy consumption and invest in sustainable computing practices.
Users can also make more ethical choices by avoiding unnecessary image generation and supporting companies committed to reducing their environmental footprint.
How AI Platforms Are Addressing Ethical Concerns:
As awareness of these ethical issues grows, some AI platforms are implementing proactive measures to promote responsible use while maintaining creative power.
Advanced AI platforms like AI Studio now incorporate ethical safeguards into their design.
These include transparent data practices, where users can understand which datasets were used for training.
Some platforms offer compensation models for artists whose work contributes to training datasets, aiming to create a more equitable ecosystem.
Content moderation features help prevent the generation of harmful, illegal, or copyright-infringing content.
Sophisticated filters block problematic prompts while still allowing creative freedom. Watermarking and metadata tracking help identify AI-generated content, promoting transparency in the digital media landscape.
User education also plays a key role. Many platforms provide guidelines that help users understand best practices, legal considerations, and ethical use cases.
Some platforms even offer tutorials on how to create diverse, unbiased prompts to avoid reinforcing stereotypes.
Best Practices for Ethical Use:
If you’re using AI image generation, here are several steps you can take to ensure ethical use:
- Be Transparent: Always disclose when images are AI-generated, especially in professional or commercial settings.
- Respect Copyright: Avoid using AI tools like AI art generators to replicate specific artists’ styles or copyrighted work. Create original concepts.
- Consider the Impact: Think about how your use of AI affects human creators. Use AI as a supplement rather than a replacement.
- Review for Bias: Examine AI-generated images for stereotypes or biased representations. Edit prompts to ensure diversity.
- Verify Accuracy: Don’t present AI-generated images as real photos or documentation of actual events. Fact-check any informational content.
- Use Responsibly: Avoid generating images that could harm individuals, spread misinformation, or violate privacy.
Also Read:
20 Generative AI Examples Across Industries
10 Useful AI Tools For Social Media
The Future of Ethical AI Image Generation:
As the conversation around AI image generation ethics continues to evolve, we can expect increased regulation, with governments and industry organizations developing frameworks to address AI-related concerns.
Technological solutions will keep improving, with better bias detection, enhanced copyright protection, and more robust content moderation.
In the future, we may see the development of “ethical AI” certifications that help users identify responsible AI tools, like GlobusSoft AI, which is making strides in promoting responsible AI development.
The creative community will also continue to adapt, finding ways to work alongside AI while preserving the value of human creativity.
Conclusion:
AI image generation offers incredible possibilities for creativity, but it also raises important ethical questions.
As users and creators, we must engage with this technology thoughtfully and responsibly.
By staying informed, practicing transparency, and supporting responsible AI development, we can help shape a future where AI enhances human creativity without undermining the rights and livelihoods of artists.
The technology itself is neutral; its ethical impact depends on how we choose to use it.
FAQ’s:
Q1: Is it legal to use AI-generated images commercially?
Ans: The legality depends on the specific AI tool and its terms of service. Some platforms grant commercial rights, but it’s important to verify the usage rights and ensure the image doesn’t infringe on copyrighted work.
Q2: Can AI replace human artists entirely?
Ans: While AI can generate impressive visuals, it lacks emotional intelligence and creativity. It serves as a tool to enhance human work rather than replace artists’ unique skills and perspectives.
Q3: How can I tell if an image is AI-generated?
Ans: Look for unusual details or inconsistencies like distorted textures or odd proportions. Specialized detection tools can also help identify AI-generated content.
Q4: Are my AI prompts and images private?
Ans: Privacy varies by platform. Review the AI tool’s privacy policy to understand how your data is used and whether it’s shared.
Q5: How does AI image generation impact the environment?
Ans: Training large AI models requires substantial computational power, contributing to high energy consumption. As AI use grows, its environmental footprint is a concern, urging sustainable practices within the industry.